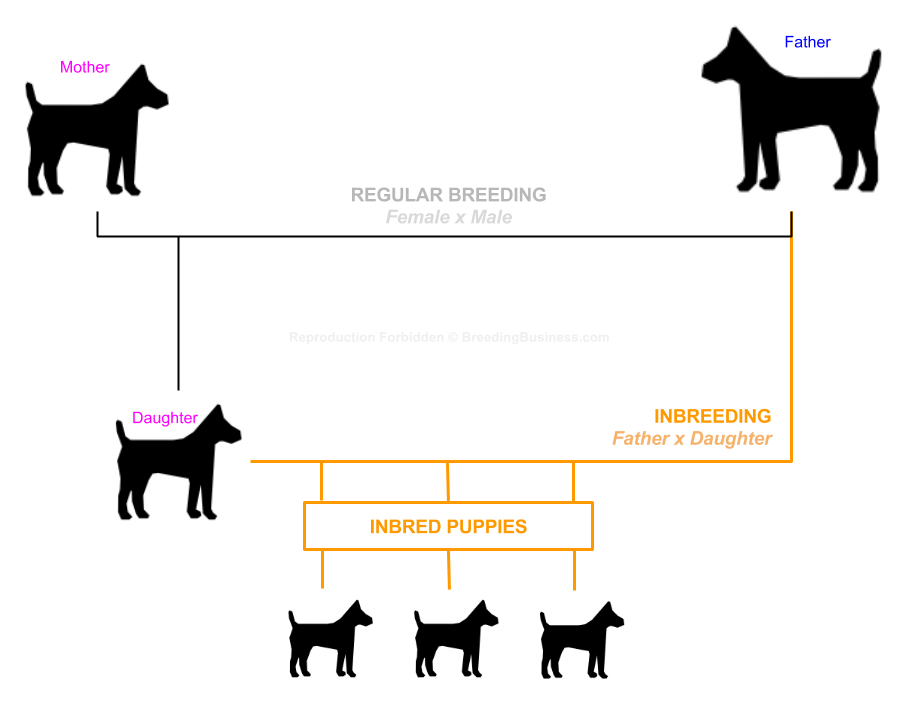
Inbreeding happens when closely related individuals breed and produce offspring. The American Kennel Club (AKC) prohibits registering directly inbred individuals like father-daughter, mother-son, and sibling combinations. Inbreeding depression is a phenomenon where the genetics of a population get weakened due to inbreeding.
When the genetics of a population get weakened due to inbreeding, it can lead to a higher probability of poor health in all individuals of the same bloodline and breed. Furthermore, there is a loss of variation, which increases the likelihood of transferring negative traits like difficulty breathing due to a small snout or hip dysplasia
What is inbreeding depression in dogs?
When closely related animals mate, their offspring may suffer from inbreeding depression. In other words, if the puppies’ parents have similar genetic makeup, the puppies may experience health issues, negative temperaments, and reduced herd immunity.
Herd immunity refers to the ability of a group of animals to resist the spread of disease. When a breed or species has genetic variation, some individuals can adapt and survive if a new disease comes along. However, when inbreeding occurs, the genetic variation decreases, making the entire breed or species vulnerable to diseases.
To summarize, inbreeding can lead to health issues, negative temperaments, and reduced herd immunity in puppies. Genetic variation is essential for developing herd immunity, and inbreeding decreases genetic variation, making a breed or species vulnerable to disease
Problems
Inbreeding depression can also affect breeding and fertility in general, both in males and females. Litters produced through inbreeding may have shorter life spans, higher rates of puppy mortality and smaller litter sizes. Furthermore, all produced puppies may have shorter lifespans due to poor physical build, weakened immune system and inherited disease. Thereby, all the produced puppies are already at a huge physical disadvantage in life. Even with preventatives such as DNA testing, problems can still arise. These tests only show up known diseases, many recessive and unknown diseases could still affect the young.
With these negatives, you may be wondering why breeders would even consider these routes? Breeders consider using inbreeding in hopes to pass on a desirable trait seen in the two individuals, such as their temperament or physical statue. For example, a well-pronounced ridge in Ridgebacks. Another example of this. Other motives may be the ease in finding two biological able dogs and thereby increasing the speed of breeding and reducing the costs. This is often why inbreeding is seen commonly in poorer countries. But the process is generally considered irresponsible and poor animal care by most breeders. Hence why the AKC prevents puppies from being registered who have been directly inbred.
What is the coefficient of inbreeding formula?
The coefficient of inbreeding depression formula is a way for breeders to predict the probability of biological risks being passed from the parents to their offspring. When a puppy possesses two of the same alleles for a given gene, this is the scientific explanation of inbreeding. F represents the coefficient of inbreeding within the formula.
The formula is: Fχ=∑[(½)N+1(1+FA)]
Without explanation, this formula can be overwhelming and confusing. To simplify it, we are going to individually explain each component and how to complete the formula.
[adwithin]
- F means the coefficient of inbreeding.
- X represents the individual you are studying.
- ∑ means ‘the sum of’. In this case, the total of (½)n+1(1+FA).
- A general rule in math is always to work out what is in the brackets first, this is important to note.
- N counts the links between the parents of X. You can count the connecting lines to do this.
- A represents the common ancestor of X’s parents.
- Therefore, FA is the coefficient of inbreeding of the common ancestor and Fχ is the coefficient of inbreeding of the individual.
The process
Now that we have explained the meaning of each component, we can take you through step by step of the process.
- Find the coefficient of X’s common ancestor through FA=∑[(½)N+1(1) as follows:
- Firstly identify the common ancestors of the two parents and use the formula on each individual that classifies as such
- This is first simplified into N+1
- Then multiply this by a 1/2
- Times This number by 1
- Then add the results of each common ancestor together to find FA
- Then you can find the coefficient of X by following the formula: Fχ=∑[(½)N+1(1+FA)]
- Follow steps 3 and 4
- Then add 1 to FA
- Multiply these two answers together and you have found your coefficient of X
Check here if you need further clarification or click here for the simple calculator!
In summary, a result of 0% indicates unrelated individuals, 12.5 indicates distant inbreeding and 25% indicates close genetic inbreeding.
What are the consequences of inbreeding depression?
Inbreeding depression consequences grow more severe with increased genetic inbreeding and time. With each generation of inbred individuals, the genetic pool is less varied, thereby leading to less well-adapted dogs. It is important to note that inbreeding affects dogs in three ways: biologically, behaviourally and through their appearance.
[adwithin]
When a dog’s biological system because less varied, it is less exposed and weakened to outside diseases. Fewer antibodies and defense systems are passed on and this leads to a weaker immune system of each inbred puppy. With similar genetics, this also increases the chances of the puppy being born with a hereditary disease as more genes carry it, thereby increasing the probability. Disease immunity and positive health may also be passed on but when individuals are inbred their experiences and genetics are not as wide-spread leading to increased chances of negative possibilities.
The most popular motivation for inbreeding is to achieve a litter with a similar aesthetic to that of the parents. Coat color, Size, muscle types, and even snout length are all possible breeding goals. However, genetic influence is a lottery and puppies may have any number of traits from either parent. This means that although the probability of the litter having the wanted traits is increased, so are any negative traits found in that family due to the inbred lines. This may mean that a litter of Boston Terriers have the ideal coat length but come out with the families well know eyesight problems.
Inbreeding can also affect puppies’ behavioral traits. The aim may be to produce a litter of high energy Labradors which is achieved, but they may also have high levels of aggression or anxiety.

How to avoid a high level of inbreeding within a gene pool?
Breeding with different dogs can help maintain the health of a breed by increasing genetic diversity. It’s important to choose the right mate for your dog, though, as not all dogs may produce healthy puppies. Cross-breeding, or breeding with a dog of a different breed, can introduce new genetics and make puppies stronger, but some experts disagree on the actual health benefits.
If breeders choose to mate dogs from the same family, they should make sure they are not closely related. This can help prevent health problems in the puppies. It’s important for breeders to take responsibility for the health of their animals and ensure that they are producing healthy puppies.

One comment on “Inbreeding Depression – Definition, COI Formula, Consequences and, Avoidance”
Does the following part of the instructions:
“Firstly identify the common ancestors of the two parents and use the formula on each individual that classifies as such”
mean that you go back on ancestors until you reach the first common ancestor and then stop at that point? Some of our dogs go back many generations before a common ancestor is located. Or do you just stop after a certain number of generations? This section is confusing me.
I have a huge database of one species of dogs and want to be able to create the COI value on the fly. I created a very fast CTE-query that pulls out the ancestors from the MySQL database to “X” number of generations. Then, I use other code to locate the common ancestor. Some of our dogs have many common ancestors depending on how far back you go generation wise.
Thanks for any help with this question!
Ernie A.